How to effectively adopt RPA and operate without failure
In Japan, with the national push towards work style reforms, requests for automating and making work more efficient are increasing. RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is software that is becoming popular for recording and reproducing the operations performed by humans, in other words, automating tasks with robots.
RPA is becoming popular in all industries
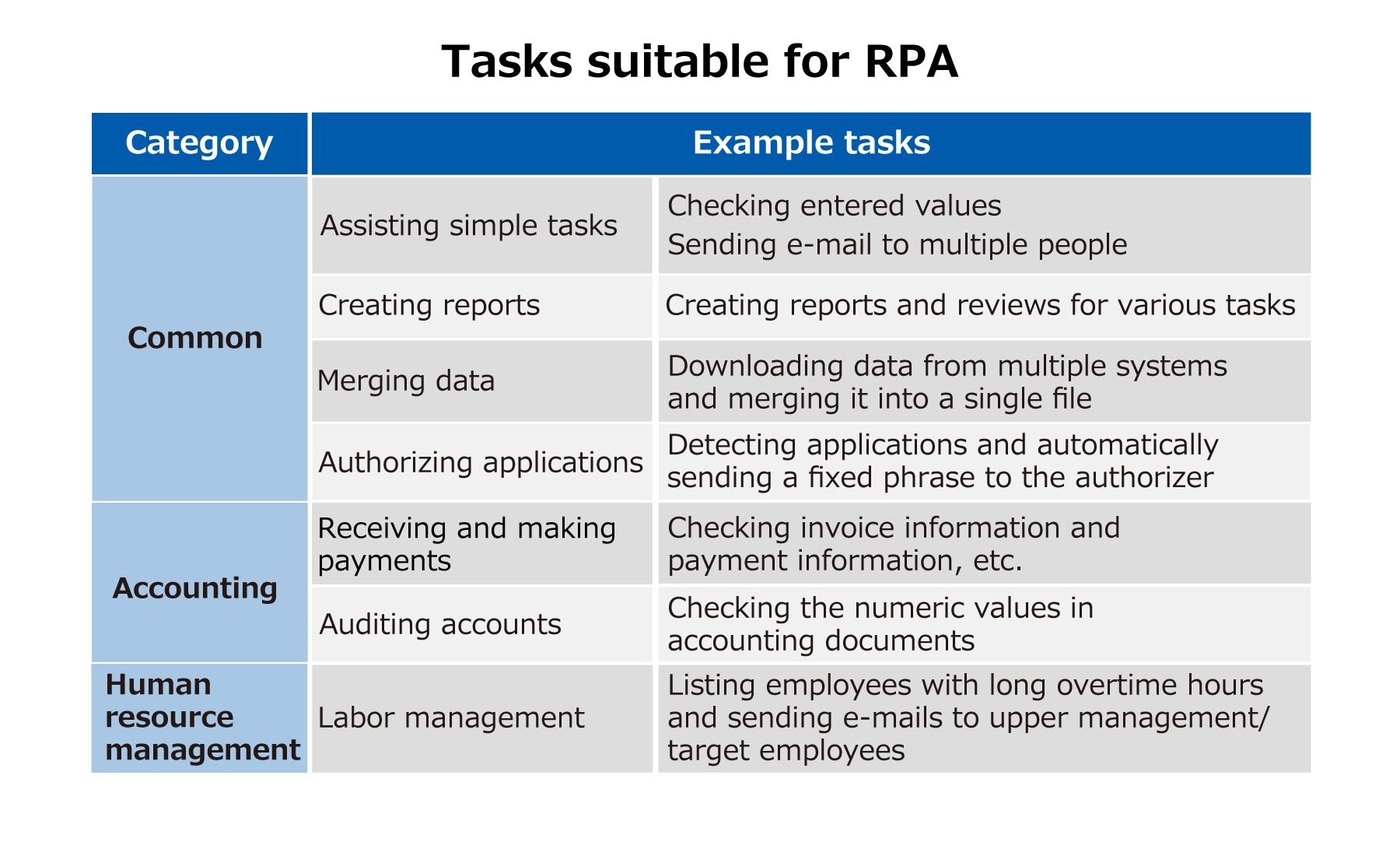
RPA is effective for simple tasks such as obtaining data from a system, entering data to a system, and performing error checks. The recording of operations is similar to the macro function of Microsoft Excel, but although macro functions perform processes within a single application, RPA enables the automation of processes across multiple systems and applications.
Three important points for adopting RPA
The number of companies that want to use RPA to improve their productivity are increasing, but companies often say that they do not know how to adopt or manage it. Nomura Research Institute (NRI) identified three important points to note when adopting RPA via PoCs (proofs of concept) created with various companies.
(1) Effect verification with a PoC
When developing business IT (IT for the purpose of business expansion), it is common to create a PoC to check the feasibility with a simple model while formulating the concept for the overall project. Adoption of RPA also requires the creation of a simple robot with limited department and work scope before increasing the scope of application while confirming the effect. Confirming the effect with a PoC also makes it easier to receive authorization from upper management in order to expand the scope of adoption.
(2) Task standardization and participation of end user departments
In order to automate tasks with RPA, it is desirable for the task rules and logic to be clear. However, in many cases the judgment standards differ by operator, there are no manuals, and the tasks are not standardized. In this case, it is important to increase the involvement of the end user department in the project and get them to understand the necessity of task standardization.
(3) Careful tool selection
It is also important to carefully select which tools to utilize for RPA adoption. Companies are prone to get the impression that complicated logic can be easily automated if they simply rely on vendor materials and demos. Since many tools can be used for free for one or two months to create a PoC, it is desirable that a company tries them out themselves to make a comparison.
Four points for continuing to operate RPA effectively
Another element required for utilizing RPA is considering governance and management for operation after adoption, in the same way that one would do with a regular system. Four points for doing so are indicated below.
(1) Allocating roles in the organization
The major tasks for robot adoption are decision making for the adoption itself, development, operational monitoring after development, and infrastructure development. In many actual cases, decision making for adoption and development are performed by the end user department and the information systems department is often in charge of operation after development and infrastructure in many cases.
(2) Organizing rules
The end user department cannot freely create robots unless rules are decided before adoption. This can lead to risks such as robots placing a burden on existing systems and robots becoming black boxes because the people that were in charge of their creation are no longer present. It is important to organize rules at the time of adoption, such as judgment rules and documentation rules.
(3) Creating a system that continues to improve development productivity
Although RPA can be easier than a regular system, it requires some degree of mastery. It is necessary to create education methods and materials, and cultivate teachers. Also, since implementation can be difficult without technical knowledge, it is effective to create libraries for the parts that perform processing frequently and can easily get stuck. Adding and sharing information as necessary can prevent other people from having trouble in the same area, and greatly enhance the productivity of development.
(4) Automation that considers problem handling
Tasks utilizing RPA need the same rules for handling problems as regular systems. If a system for handling problems cannot be created, then it may be better to avoid the adoption of RPA itself.
The potential for RPA to change business
RPA is currently mostly adopted in tasks with clear rules, but it is thought that combining it with AI in the future will enable robots that can make complicated decisions. In our joint research conducted with a certain company, we have been examining the possibility of creating a system for automating work that requires complicated decision-making by allowing AI to learn atypical data and converting it into the typical data that RPA is good at handling. Although RPA is simple and has limitations due to that simplicity, it is showing promise as a system that will increase competitiveness by combining it with other technologies to enable the automation of a wide range of tasks.
Profile
-
Yuta Ichihara
* Organization names and job titles may differ from the current version.